Protecting Highly-Impacted Communities
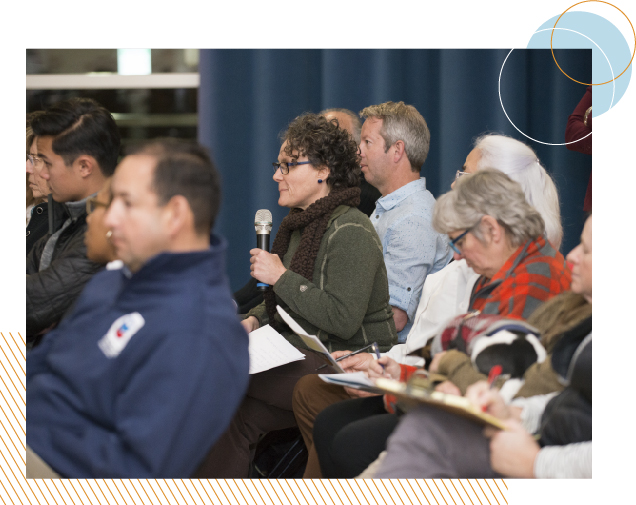
The Air District hosted a series of community workshops to begin implementation of state law AB 617, which requires local air districts to continue to reduce air pollution exposure in the most impacted communities. The Air District held four workshops to discuss community-level monitoring and planning in highly impacted Bay Area neighborhoods.